Move Exchange Server to New Server Using Database Portability
Moving the mailboxes across servers is not much difficult task to be carried out. However, the process to migrate Exchange 2007/2010/2013 Server to new Server is the one, which needs some extra efforts to be carried away. The specific edition of the Exchange server comes up with a feature known as Database Portability to move Exchange Server to New Server. It permits migration of Exchange 2007, 2010, 2013 mailbox database to other server within the same organization by simply mounting or moving process.
This server destination database should have same schema edition in its database. Earlier versions of Microsoft Exchange Server cannot transfer mailbox database into mailbox server operating on MS Exchange 2013 edition. With the utilization of database portability feature, data enhancement in reliability is possible by the removal of error-prone steps of data recovery. Not only this, database portability also occurs to decrease the complete data recovery time objective for a number of circumstances of failure.
Database portability can be utilized for transferring mailbox database between Exchange 2007, 2010, 2013 of the similar network. Therefore, numerous of recovery time objective is decreased for specific scenarios containing failure.
Prerequisites to Move Exchange Server to New Server
You must know basic things before proceeding to the process of migrating Exchange Server to any new server. These are the following things you should be aware of:
1. EAC cannot be utilized for transferring user mailbox to the dial-tone database or even a healthier database by Database Portability.
2. The expected time essential for transferring would be approx. 5 minutes without time taken for data restoration, moving database, and waiting for the replication of Active Directory to complete.
3. It is important to have correct permissions before execution.
Technique to Migrate Mailbox by Database Portability
Move Exchange Server to New Server by the following steps:
1. You should approve that the database that has to be transferred is in the condition of clean shut down beforehand. In case it is not, it is recommended to perform the soft recovery.
Important: While performing the soft recovery, all the log files should be in an uncommitted state and should be devoted to the particular database automatically. In case, you are not present with essential log files, the soft recovery process cannot be concluded.
2. For simply committing the uncommitted logs to your Exchange database, run the mentioned command from command prompt.![]() NOTE: indicates the prefix of log files for the target database, i.e. one in which you are proposed to commit log file. This is an important parameter while executing the command Eseutil /r.
NOTE: indicates the prefix of log files for the target database, i.e. one in which you are proposed to commit log file. This is an important parameter while executing the command Eseutil /r.
3. Utilize the syntax, which is given below for generating new database: 4. Allocate ‘this database can be overwritten by restore attribute’ and move Exchange Server to New Server by using the mentioned syntax:
4. Allocate ‘this database can be overwritten by restore attribute’ and move Exchange Server to New Server by using the mentioned syntax: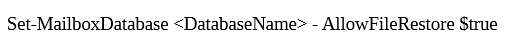 5. Now, begin transferring the unique copy of database files that includes LOG, EDB, and search catalog of Microsoft Exchange to stated destination folder.
5. Now, begin transferring the unique copy of database files that includes LOG, EDB, and search catalog of Microsoft Exchange to stated destination folder.
6. Mount your Exchange database by using the mentioned syntax:![]()
Once your Exchange database is completely mounted, start with modifying settings of the user account by using – Set-Mailbox cmdlet. This means the account will point to Exchange mailbox on the new server. Use the mentioned syntax to migrate Exchange 2007/2010/2013 to a new Server of the users from old to new:
 7. The mentioned syntax will benefit in triggering delivery of messages, which are still pending in the queue.
7. The mentioned syntax will benefit in triggering delivery of messages, which are still pending in the queue.![]()
Once replication procedure of Active Directory completes, all the users will finally be capable of getting utilization to their own mailboxes present on the new (destination) Microsoft Exchange Server database. Many clients are readdressed with help of Autodiscover. The OWA users are redirected automatically too.
Confirming the Move
To cross-check whether the migration was successful or not, execute the following:
1. Open your Exchange mailbox on Outlook Web App
2. Open the mailbox with MS Outlook client
By opening any of these platforms, users will see that the Exchange mailboxes is successfully moved to the new Exchange server.
Note: If you are new to the Microsoft Exchange environment then it would be very difficult for users to understand all the technicality and working of the server because it requires in-depth knowledge, technical skill, and hand-on experience to handle the server. So, to avoid all the complexity users can use the advanced solution given in the below section which easily move the offline/dismounted Exchange database mailboxes to the Live Exchange Server mailboxes in a simplified manner.
Rapid Solution: Exchange to Exchange Migration tool supports offline/dismounted EDB file and easily move the mailboxes of one Exchange Server to the new one from offline Exchange database file in a hassle-freeway. Users can load .edb file and export mailbox from offline Exchange database to the selected Exchange Server version. It provides Quick and Advance scanning mode which automatically repair and recover corrupt Exchange database files with no data loss, you can select the options according to the level of corruption in EDB file. After recovery, users can export the healthy and recovered mailboxes to the Live Exchange Server 2016/2013/2010/2007/2003, Office 356, and different file formats. Users can easily export Exchange 2003 mailbox to Exchange 2010 or any other versions by using this software.
Conclusion
The above-discussed method is a reliable method to move Exchange server to new Server manually. However, in the state of not being happy in the mounting database between the Exchange servers by using Database Portability way, commercial solutions Exchange to Exchange migration software described in the above section. The tool consists of many features that can make your migration process easy and help you in saving a single bit of data. The solutions have an added benefit of executing on the disconnected database that avoids putting the Exchange server in downtime.



